HISTORY OF
PAKUR
Pakur in its emergence and inception had been a cluster of
ponds and orchards surrounded by deep forest and hard rocks
under the range of Rajmahal hills. It had previously been
Raj in its new dimension under the British rule. The British
had also been the centre of revolutionary activities, the
repercussions of which might be seen in the Santhal Hul of
1855.
There is evidence of area having been inhabited since very
early times. Among the early settlers of their territory of
whom there is any record, are the Maler (Sauria Paharias)
who still inhabit some areas of Rajmahal hills and its
adjoining hilly tracts. They have been identified with
“Malli” period of Chandragupta Maurya. According to him the
Malli were a race holding the country between the people of
Magadh and the people of lower Bengal. A reference has also
been found in the travel account of Hiuen Tsiang, the
Chinese pilgrim, who visited India about 645 AD. From the
record of his travels it is learnt that he visited the
kingdom of Champa, the Northern boundary of which extended
along the Ganges from Lakhisari to Rajmahal hills while the
Southern boundary passed through desert wilds in which were
wild elephants and savage beasts that roamed in herds. To
the east of Champa lay the kingdom of Kie-Ching Kielo, which
according to General Cunningham was the tract of the country
included in the present Santhal Pargana.
After the downfall of Harshavardhan, the king of North India
upto the advent of Mohammedans rules in 12th Century this
area remained in oblivion due to its deep forests and
inaccessible passes. The authentic history of the area may
be said to begin with rule of the Mohammadans when their
armies marched to and from Bengal through the Teliagarhi
pass. According to Mohammedans historians Teligarhi pass the
“key of Bengal” as it was called, was the scene of numerous
battles. The next important event in the history of this
area was the establishment of Rajmahal as the capital of
Bengal in 1592 to signalize the importance of the Mughal
victory. The Mughal Govt. seeing the little prospects of
revenue from these barren hills had been content to leave
control of them to Mansabars of whom the chief were the
Khatauri family of Manihari. The founder of the family
helped Raja Man Singh, the reputed general of Mughal emperor
Akbar in Bengal invasion. In reward he got the office of
Mansab Jagir of the tract Rajmahal and Pakur on the east of
the hills to Kahalgaon and Godda on their western face.
Whether the control they exercised was effective or, as is
more probable.
INTRODUCTION
Organizational Background

Foundation for Awareness, Counseling and Education (FACE) is
a NGO based at Pakur (a district located in the north east
corner of Jharkhand bordering Murshidabad) district of West
Bengal which is working among the local disadvantaged
community with a vision to form “an enlightened & empowered
society” through education, Health Awareness, community
based income generation programmes since January 2001. FACE
got registered on 14th January, 2002 under Societies
Registration Act 1860, XXI. Under the societies byelaws it
is committed to discrete a set of activities and inputs such
as eradication of illiteracy, poverty, social abuse etc. The
vision is to create a self reliant equitable, value based
educated society through social transformation, empowerment
of deprived rural population. FACE has been working in six
blocks of Pakur district with special focus on children,
women, youths of local tribals (Santhals & Paharia) and
Muslim minority community. The region is also significantly
under developed due to absence of industries and allied
sectors. Majority of the population are dependent on
Agriculture, Cattle Rearing, Mining (stone quarries & coal
mines) and Forest for their livelihood.
The journey of FACE started with the set up of “Shaishav”, a
drop in centre for children of local disadvantaged
community. Gradually, FACE has gained recognition in Pakur
by making its presence felt in various programmes on health
and hygiene, education at different locations in Pakur
district.
Though geographical area of operation of FACE is primarily
limited to Pakur and its neighboring blocks but, its
operation in terms of reach and coverage has increased over
time. Organizing various activities like district level
training, sensitization workshops for various stakeholders
FACE has now come to the limelight in the District.
Successful implementation of programmes with support of Govt.
of Jharkhand
and adequate media coverage have also helped FACE to earn
reputation at state level.
Along with Schedule Tribes & Muslim minorities, women have
been given special focus throughout the journey of the
organization. The poor economic & social plight of
population in the district is the obvious reason for FACE to
choose this district- Pakur as a work area, based the
notion, “if you want to change the world, first change your
home”.
VISION & MISSION
The vision for FACE is “Forming an Enlightened and Empowered
Society”. The mission of the organization is as follows:
-
Imparting
basic education to children to ensure their right to
education
-
Generating awareness on health & hygiene issues and
reproductive and sexual health
-
Breaking
myths and misconceptions of the community on health and
education
-
Working
against gender discrimination, gender violence through
women empowerment & making them self-reliant
-
Functional Education for Adult Women
-
Promoting
Girls Children Education
-
Skill
Development training and Financial inclusion initiative
for socially excluded men and women
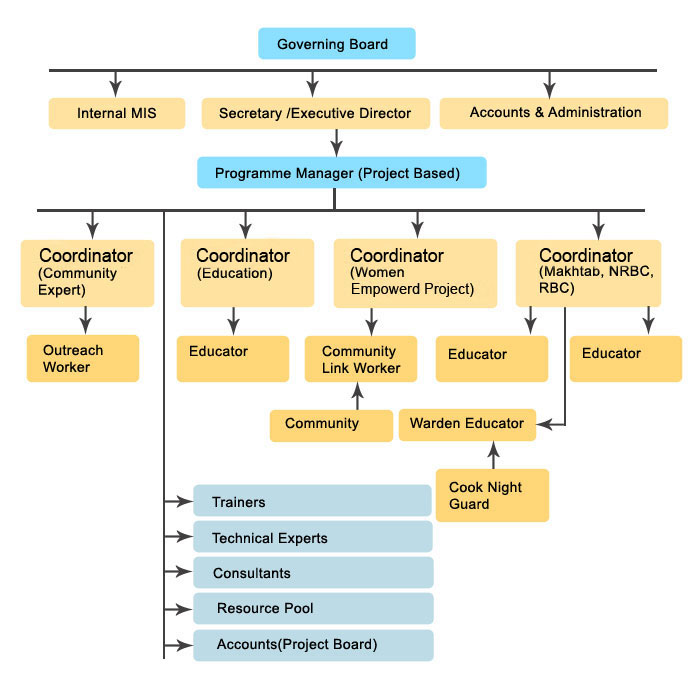
ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE AND PROTOCOL
FACE has an executive committee consisting of Nine members
who are responsible to run the organization. This committee
also selects the secretary who overall looks after the
coordination of work, activities and program. The following
table shows the hierarchical structure of the organization.
LEGAL STATUS
Registration
Registration
Act, 1860 Regd. No. 192 dated on 14 January 2002:
-
u/s 12A of
Income Tax Act, 1961
-
FACE is
registered under section 4 (1) (b) of foreign contribution
& regulation act, 1976 (FCRA registration no: 337780015)
-
PAN No :
AAAAF0410E
-
TAN No :
RCHF00102E
-
80 G : SSAA/
Dhanbad/Tech/80G-7/2013-4/589-92
EPF Details
(Extract of Form 5A under EPFO para 78(3):
-
EPF Code- JHRAN3273492000
-
Registered Name- Foundation for Awareness Counselling and Education
-
Date of coverage- 01-05-2024
-
No. of Branches & Primary Br. Address- One(1)
Foundation for Awareness Counselling and Education
Rajapara, Pakur , Jharkhand-816107
-
Regional office - Ranchi, Jharkhand
GOVERNING
BOARD MEMBERS OF FACE :